The JSON format is an open standard format. The format of data looks very easy to understand and the data objects consist of attribute-value pairs.

ContentEncoding: It helps to indicate the content encoding type, the default encoding for JSON is UTF-8.
ContentType: It helps to indicate the content type. The default content type for JSON is application/json; charset=utf-8.
Note: ContentType and ContentEncoding are not necessary to mention when sending the data in JSON format as the HTTP headers are having a responsibility to tell the recipient what kind of content they're dealing with.
Data: This indicates what the content data is, that means what you will send in JSON format.
JsonRequestBehavior: This property has two options. Those are AllowGet and DenyGet. The default option is DenyGet. When you send data in JSON format, using Get Request, it's necessary to specify the property as AllowGet otherwise it shows the error as “The request would be blocked since the JSON data is considered as sensitive data information”.
MaxJsonLength: This helps to get or set the maximum JSON content length that you will send. The default value for this is 2097152 characters, that is equal to 4 MB of Unicode string data. You can even increase the size based if needed, for that you will get an idea later in this article.
RecursionLimit: Indicates the constraining number of object levels to process. The default value is 100. It means you can serialize the objects that are nested to a depth of 100 objects referencing each other. In a general scenario, the default limit 100 is obviously sufficient when you deal with a JsonResult so there is no need to increase it even though you have the option to increase the limit if required.
Sample Project with Various Scenarios by using JsonResult
Create a new project with the name JsonResultDemo and choose the template as MVC as shown in the following screenshots.
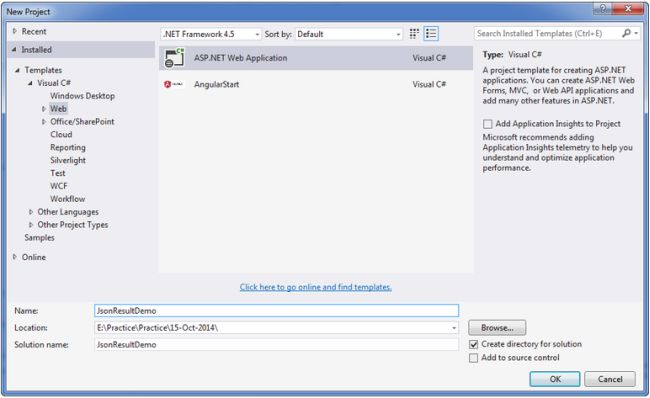
Now, click on the OK button then the displayed screen is as in the following.
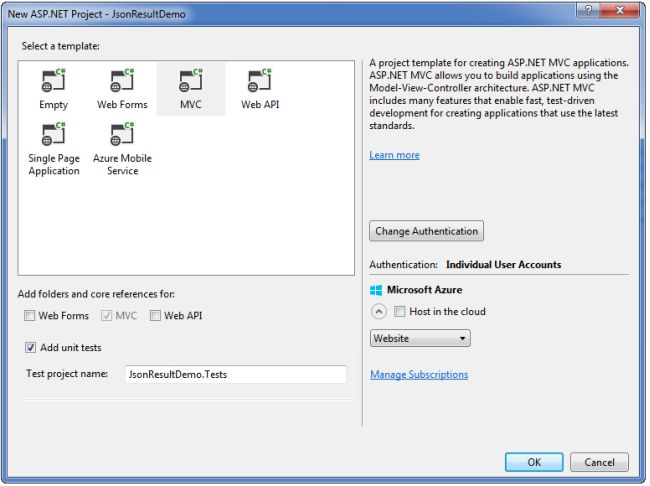
As in the preceding template, you need to select the “Add Unit Tests” option as well. So It helps to create a Unit Test project and then again click on the OK button then the project will be created and the startup application page displayed like the following.
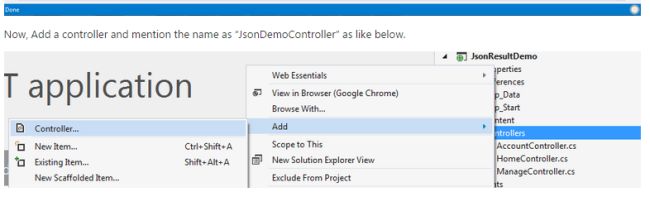
Now, add a controller and provide the name as “JsonDemoController” as in the following.
Click on the Controller and then it will open the popup window as in the following.
Now, click on the “Add” button and then it opens a popup to enter the name. So enter the name as “JsonDemoController” as shown in the screenshot.
After adding the controller to the project the controller page looks like the following.
Until now, you are done with the creation of the sample project template with the addition of one controller named “JsonDemoController”.
Scenario 1: Send JSON Content welcome note based on user type
In this scenario, you will learn how to send a simple welcome note message in JSON format from the controller. Now, replace the existing code with the following code in the JsonDemoController.cs file.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.Web.Script.Serialization;
using JsonResultDemo.Models;
namespace JsonResultDemo.Controllers
{
public class JsonDemoController : Controller
{
#region ActionControllers
/// <summary>
/// Welcome Note Message
/// </summary>
/// <returns>In a Json Format</returns>
public JsonResult WelcomeNote()
{
bool isAdmin = false;
//TODO: Check the user if it is admin or normal user, (true-Admin, false- Normal user)
string output = isAdmin ? "Welcome to the Admin User" : "Welcome to the User";
return Json(output, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
}
}
Then, build the application (F6) and then hit the F5 to run an application and then navigate to the following URL http://localhost:49568/JsonDemo/WelcomeNote (It might be a chance to get a different Port Id at your end).
Then the displayed screen looks like the following.
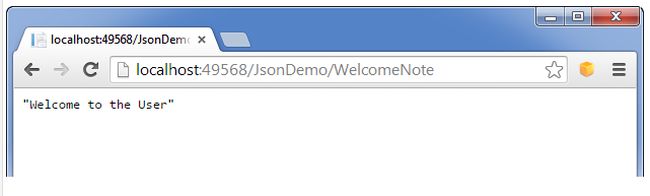
In this scenario, you now have an idea of how to send a simple string in JSON format.
Scenario 2: Get the list of users in JSON Format
In this scenario, you will send a list of users in JSON format.
Step 1: Add a class file “UserModel.cs” like the following.
Click on “Class” and then the displayed link is as the following.
Enter the name as “UserModel.cs” and then click on the Add button.
Step 2: Update the code in UserMode.cs with the following code.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
namespace JsonResultDemo.Models
{
public class UserModel
{
public int UserId { get; set; }
public string UserName { get; set; }
public string Company { get; set; }
}
}
Step 3: Add one method named GetUsers in the JsonDemoController.cs file that will return the list of sample users.
/// <summary>
/// Get the Users
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private List<UserModel> GetUsers()
{
var usersList = new List<UserModel>
{
new UserModel
{
UserId = 1,
UserName = "Ram",
Company = "Mindfire Solutions"
},
new UserModel
{
UserId = 1,
UserName = "chand",
Company = "Mindfire Solutions"
},
new UserModel
{
UserId = 1,
UserName = "Abc",
Company = "Abc Solutions"
}
};
return usersList;
}
Step 4: Create one Action Controller method named GetUsersData with the following code in the JsonDemoController.cs file.
/// <summary>
/// Get tthe Users data in Json Format
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public JsonResult GetUsersData()
{
var users = GetUsers();
return Json(users, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
Step 5: Run the application with this URL http://localhost:49568/JsonDemo/GetUsersData then the output looks like the following.
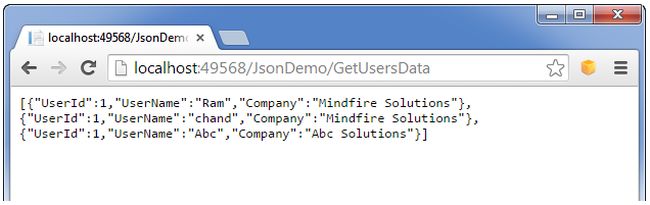
Scenario 3: Create JSON data at the client side and send content to the controller
In this scenario, you will create JSON data at the client side and then that data will be sent to the Controller action. The controller action request type is HttpPost.
Step 1: Create one Action controller method named Sample like the following in the JsonDemoController.cs file.
/// <summary>
/// Sample View
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public ActionResult Sample()
{
return View();
}
Step 2: Create a View file named “Sample.cshtml” by right-clicking on View() in the Sample action controller method then click on “Add View” in the Sample action like the following.
By clicking on Add View it opens a popup and deselects the "Use a layout page" option. It then should look as in the following.
Now, click on the OK button then the sample.cshtml file will be created.
Step 3: Replace it with the following cshtml code in the sample.cshtml file.
@{
Layout = null;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>Create Sample JSON Data and send it to controller</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<label>Create Sample User JSON Data and send it to controller</label><br/><br />
<input type="button" id="btnUpdateUserDetail" value="Update User Detail" onclick="UpdateUserDetail();"/>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<script src="~/Scripts/jquery-1.10.2.min.js"></script>
<script lang="en" type="text/javascript">
function UpdateUserDetail() {
var usersJson = GetSampleUsersList();
var getReportColumnsParams = {
"usersJson": usersJson
};
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
traditional: true,
async: false,
cache: false,
url: '/JsonDemo/UpdateUsersDetail',
context: document.body,
data: getReportColumnsParams,
success: function (result) {
alert(result);
},
error: function (xhr) {
//debugger;
console.log(xhr.responseText);
alert("Error has occurred..");
}
});
}
function GetSampleUsersList() {
var userDetails = {};
var usersList = [];
for (var i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
userDetails["UserId"] = i;
userDetails["UserName"] = "User- " + i;
userDetails["Company"] = "Company- " + i;
usersList.push(userDetails);
}
return JSON.stringify(usersList);
}
</script>
The following is a brief description of the Sample.cshtml file:
The HTML body contains a label, about, to describe the functionality and one input button with an onclick of the UpdateUserDetail() function.
The JavaScript part contains the jQuery reference and it contains two functions.
GetSampleUsersList() will return the sample users in a stringified JSON format.
UpdateUserDetail() sends the ajax request of post type for JsonDemoController with UpdateUserDetail action.
Step 4: A Create Action method named UpdateUsersDetail in the JsonDemoController as in the following and put a breakpoint in this method on the first line of code to help to trace the details.
/// <summary>
/// Update the user details
/// </summary>
/// <param name="usersJson">users list in JSON Format</param>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpPost]
public JsonResult UpdateUsersDetail(string usersJson)
{
var js = new JavaScriptSerializer();
UserModel[] user = js.Deserialize<UserModel[]>(usersJson);
//TODO: user now contains the details, you can do required operations
return Json("User Details are updated");
}
Step 5: Build and run the application (hit F5) with the URL (http://localhost:49568/JsonDemo/Sample) then the resultant screen looks like the following.
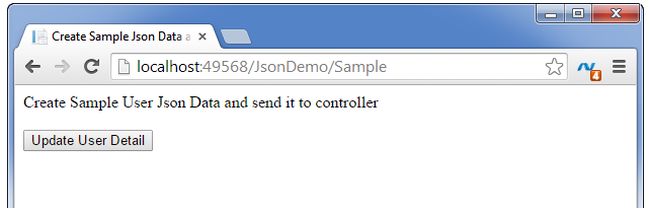
Step 6: Now, click on the “Update User Detail” button as it appears in the aforesaid screenshot. Then the resultant screen looks like the following.
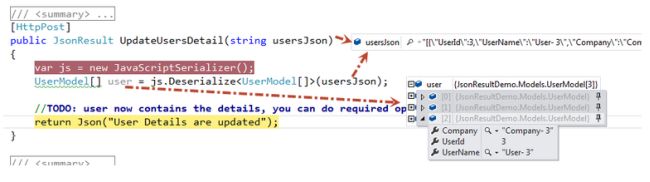
Step 7: Just review the preceding image, you can identify that you are able to send the JSON data to the controller action from the client side and as well as you have deserialized the JSON data and assigned that data to the UserModel entity.
Scenario 4: How to handle a huge amount of JSON Data
In this scenario, you will get an idea of how to send a huge amount of JSON Data. Actually, in certain scenarios, you must send a huge amount of data from a controller to a view. In that case, the following example will be helpful to you.
Step 1: Create one method named GetUsersHugeData() as in the following. It just helps to generate sample user data.
/// <summary>
/// Get the huge list of users
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private List<UserModel> GetUsersHugeData()
{
var usersList = new List<UserModel>();
UserModel user;
for (int i = 1; i < 51000; i++)
{
user = new UserModel
{
UserId = i,
UserName = "User-"+i,
Company = "Company-"+i
};
usersList.Add(user);
}
return usersList;
}
Step 2: Create an Action method named GetUsersHugeList() like the following in the JsonDemoController.cs file.
/// <summary>
/// Get the huge list of Users
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public JsonResult GetUsersHugeList()
{
var users = GetUsersHugeData();
return Json(users, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
Step 3: Now, build and run (hit F5) the application with the URL (http://localhost:49568/JsonDemo/GetUsersHugeList) then the error screen appears like the following.
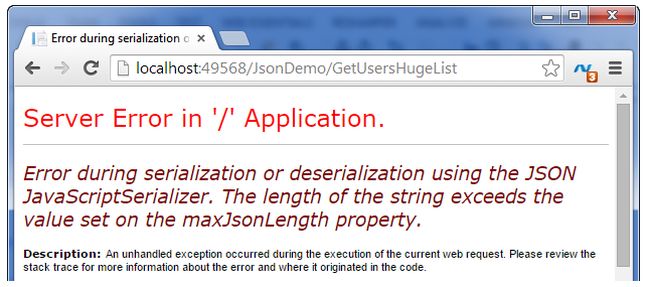
Step 4: To fix the preceding error add the following code in the JsonDemoController file. This methods helps to update the MaxJsonLength property value to Int32.MaxValue.
/// <summary>
/// Override the JSON Result with Max integer JSON lenght
/// </summary>
/// <param name="data">Data</param>
/// <param name="contentType">Content Type</param>
/// <param name="contentEncoding">Content Encoding</param>
/// <param name="behavior">Behavior</param>
/// <returns>As JsonResult</returns>
protected override JsonResult Json(object data, string contentType,
Encoding contentEncoding, JsonRequestBehavior behavior)
{
return new JsonResult()
{
Data = data,
ContentType = contentType,
ContentEncoding = contentEncoding,
JsonRequestBehavior = behavior,
MaxJsonLength = Int32.MaxValue
};
}
In the same way, you can increase the RecursionLimit property value. Also if you require JsonData with a depth (nested levels) greater than 100.
Step 5: Now, build and run (hit F5) the application with the URL (http://localhost:49568/JsonDemo/GetUsersHugeList) and then the huge data result appears instead of an error.
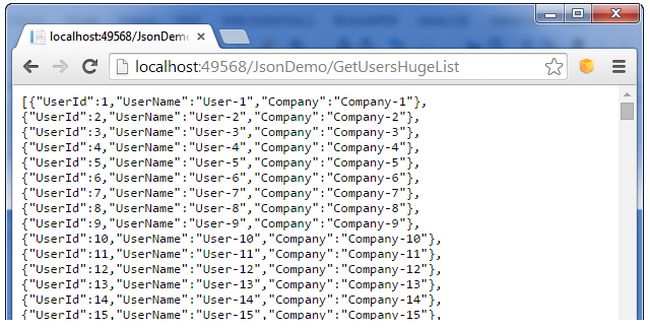
I have provided the formatted complete code for the JsonDemoController.cs file for what you have done until now in the aforesaid scenarios.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.Web.Script.Serialization;
using JsonResultDemo.Models;
namespace JsonResultDemo.Controllers
{
public class JsonDemoController : Controller
{
#region ActionControllers
/// <summary>
/// Welcome Note Message
/// </summary>
/// <returns>In a JSON Format</returns>
public JsonResult WelcomeNote()
{
bool isAdmin = false;
//TODO: Check the user if it is admin or normal user, (true-Admin, false- Normal user)
string output = isAdmin ? "Welcome to the Admin User" : "Welcome to the User";
return Json(output, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
/// <summary>
/// Get tthe Users data in JSON Format
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public JsonResult GetUsersData()
{
var users = GetUsers();
return Json(users, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
/// <summary>
/// Sample View
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public ActionResult Sample()
{
return View();
}
/// <summary>
/// Update the user details
/// </summary>
/// <param name="usersJson">users list in JSON Format</param>
/// <returns></returns>
[HttpPost]
public JsonResult UpdateUsersDetail(string usersJson)
{
var js = new JavaScriptSerializer();
UserModel[] user = js.Deserialize<UserModel[]>(usersJson);
//TODO: user now contains the details, you can do required operations
return Json("User Details are updated");
}
/// <summary>
/// Get the huge list of Users
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public JsonResult GetUsersHugeList()
{
var users = GetUsersHugeData();
return Json(users, JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
#endregion
#region Methods
/// <summary>
/// Get the Users
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private List<UserModel> GetUsers()
{
var usersList = new List<UserModel>
{
new UserModel
{
UserId = 1,
UserName = "Ram",
Company = "Mindfire Solutions"
},
new UserModel
{
UserId = 1,
UserName = "chand",
Company = "Mindfire Solutions"
},
new UserModel
{
UserId = 1,
UserName = "Abc",
Company = "Abc Solutions"
}
};
return usersList;
}
/// <summary>
/// Get the huge list of users
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private List<UserModel> GetUsersHugeData()
{
var usersList = new List<UserModel>();
UserModel user;
for (int i = 1; i < 51000; i++)
{
user = new UserModel
{
UserId = i,
UserName = "User-"+i,
Company = "Company-"+i
};
usersList.Add(user);
}
return usersList;
}
/// <summary>
/// Override the Json Result with Max integer JSON lenght
/// </summary>
/// <param name="data">Data</param>
/// <param name="contentType">Content Type</param>
/// <param name="contentEncoding">Content Encoding</param>
/// <param name="behavior">Behavior</param>
/// <returns>As JsonResult</returns>
protected override JsonResult Json(object data, string contentType,
Encoding contentEncoding, JsonRequestBehavior behavior)
{
return new JsonResult()
{
Data = data,
ContentType = contentType,
ContentEncoding = contentEncoding,
JsonRequestBehavior = behavior,
MaxJsonLength = Int32.MaxValue
};
}
#endregion
}
}
You now have an idea of how to use a JsonResult type in MVC application with various scenarios. Now, it's time to test the controller action methods using the JsonDemoController.Test project.
Unit Testing the JsonResult in MVC
The main feature of MVC applications is it supports the Test Data Driven (TDD) approach. Since the Controller file is just a kind of class file, it's easy to implement the Test methods in the Test Project. Now you will learn how to test the JsonResult methods in the test project.
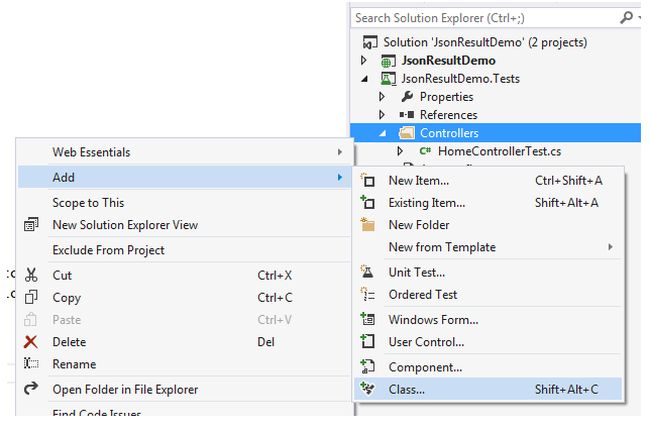
Step 1: Add a class file named “JsonDemoControllerTest.cs” to the JsonResultDemo.Tests projects like the following.
Click on “Class” to open a popup like the following and then update the name as “JsonDemoControllerTest.cs”.
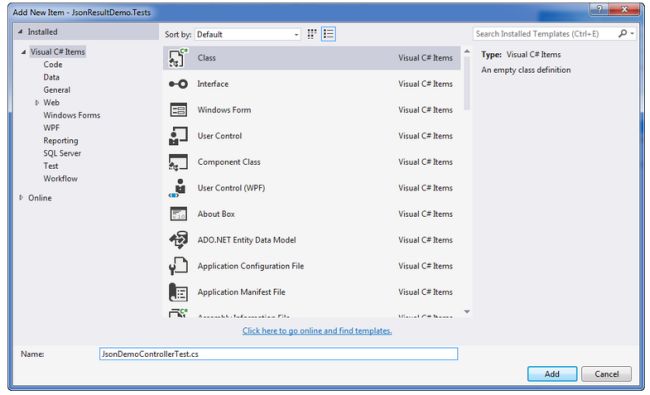
Step 2: After clicking on the “Ok” button then the screen result looks like the following.
Step 3: Now, replace the existing code in the file JsonDeomControllerTest.cs with the following code.
using System;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using JsonResultDemo.Controllers;
namespace JsonResultDemo.Tests.Controllers
{
[TestClass]
public class JsonDemoControllerTest
{
[TestMethod]
public void WelcomeNote()
{
JsonDemoController controller = new JsonDemoController();
JsonResult result = controller.WelcomeNote();
string msg = Convert.ToString(result.Data);
// Assert
Assert.AreEqual("Welcome to the User", msg);
}
}
}
Brief Note about TestMethod of WelcomeNote()
Create an object for JsonDemoController.
Save the result of JsonDemoController controller method “WelcomeNote” method result in the “result” parameter of the type JsonResult.
The string “msg” is assigned with the value from the JSON Result (result.Data).
In this step, you are checking the expected output with the actual output using the Assert method. In a similar way, the Assert Method provides other options like AreNotEqual, AreSame, IsNotNull and so on.
Step 4: Right-click on the WelcomeNote method and click on “Run Unit Tests” then the screen result looks like the following.
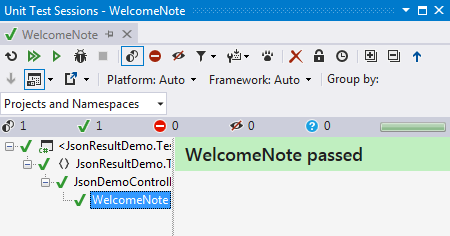
Step 5: You can also do the “Run Tests” by the clicking of (Ctrl +R, T). Then you can view the results in Test Explorer like the following.
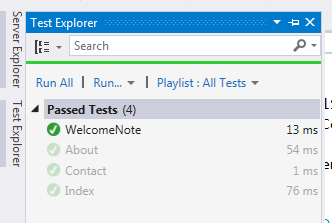
In a similar way, you can create more test methods and it will be helpful to check the functionality in various cases since it provides correct results or not. I hope this article gives you an idea of JsonResult, JsonResult Properties, the usage of JsonResult with various scenarios and how can you test the JsonResult using the Test Project.