As we all know, HTTP is a stateless protocol, i.e., each HTTP request does not know about the previous request. If you are redirecting from one page to another page, then you have to maintain or persist your data so that you can access it further. To do this, there were many techniques available in ASP.NET like ViewState, SessionState,

ApplicationState etc.
ASP.NET MVC also provides state management techniques that can help us to maintain the data when redirecting from one page to other page or in the same page after reloading. There are several ways to do this in ASP.NET MVC -
Hidden Field
Cookies
Query String
ViewData
ViewBag
TempData
The above objects help us to persist our data on the same page or when moving from “Controller” to “View” or “Controller” to Controller”. Let us start practical implementation of these so that we can understand in a better way.
Hidden Field
It is not new, we all know it from HTML programming. Hidden field is used to hide your data on client side. It is not directly visible to the user on UI but we can see the value in the page source. So, this is not recommended if you want to store a sensitive data. It’s only used to store a small amount of data which is frequently changed.
The following code is storing the Id of employee and its value is 1001.
@Html.HiddenFor(x=>x.Id)
If you open the page source code for that page in the browser, you will find the following line of code, which is nothing but the HTML version of the above code with value. Just focus on last three attributes.
<input data-val="true" data-val-number="The field Id must be a number." data-val-required="The Id field is required." id="Id" name="Id" type="hidden" value="1001" />
Cookies
Cookies are used for storing the data but that data should be small. It is like a small text file where we can store our data. The good thing is that a cookie is created on client side memory in the browser. Most of the times, we use a cookie for storing the user information after login with some expiry time. Basically, a cookie is created by the server and sent to the browser in response. The browser saves it in client-side memory.
We can also use cookies in ASP.NET MVC for maintaining the data on request and respond. It can be like the below code.
HttpCookie cookie = new HttpCookie("TestCookie");
cookie.Value = "This is test cookie";
this.ControllerContext.HttpContext.Response.Cookies.Add(cookie);
Here, we have created one cookie and named it as “TestCookie”. We can create multiple cookies and add with Response. For getting the value from an existing cookie, we first need to check that the cookie is available or not; then, we can access the value of the cookie.
if (this.ControllerContext.HttpContext.Request.Cookies.AllKeys.Contains("TestCookie"))
{
HttpCookie cookie = this.ControllerContext.HttpContext.Request.Cookies["TestCookie"];
ViewBag.CookieMessage = cookie.Value;
}
Cookies are all depended on expiry, you can create a cookie on one action method in a controller and it will save on the client side and can be accessed in another action method easily.
Query String
In ASP.NET, we generally use a query string to pass the value from one page to the next page. Same we can do in ASP.NET MVC as well.
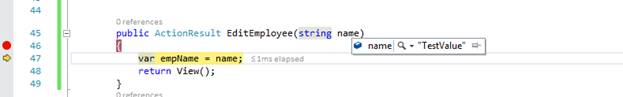
http://localhost:49985/home/editemployee?name=TestValue
I am making one request with the above URL. You can see that in this, I am passing name’s value as a query string and that will be accessible on “EditEmployee” action method in “Home” controller as the following image shows.
ViewData
It helps us to maintain your data when sending the data from Controller to View. It is a dictionary object and derived from ViewDataDictionary. As it is a dictionary object, it takes the data in a key-value pair.
Once you create ViewData object, pass the value, and make redirection; the value will become null. The data of ViewData is not valid for next subsequent request. Take care of two things when using ViewData, first, check for null and second, check for typecasting for complex data types.
public ActionResult Index()
{
Employee emp = new Employee()
{
Id = 1001,
Name = "Peter",
Address = "London",
Age = 25
};
ViewData["Message"] = "This is ViewData";
ViewData["Emp"] = emp;
return View();
}
The above code contains two ViewData dictionary objects - ViewData["Message"] and ViewData["Emp"]. The first one is a simple string value but the next one contains complex employee data. When the View is going to render, we need to first check the ViewData for null and if it is not, then we can get the value.
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Home Page";
}
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">
<h2>Employee Details</h2>
<br />
<p>
@if(ViewData["Message"] !=null)
{
<b>@ViewData["Message"].ToString();</b>
}
</p>
<br />
@if (ViewData["Emp"] != null)
{
var emp = (MVCStateManagement.Models.Employee)ViewData["Emp"];
<table>
<tr>
<td>
Name :
</td>
<td>
@emp.Name
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Address :
</td>
<td>
@emp.Address
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Age :
</td>
<td>
@emp.Age
</td>
</tr>
</table>
}
</div>
</div>
Note
If you are using ViewData that is not defined on Controller, then it will throw an error; but with ViewBag, it will not.
Do not use ViewBag and ViewData with the same name, otherwise, only one message will display. See the following code in the controller is using both ViewData and ViewBag with same name “Message”.
public ActionResult Index()
{
ViewData["Message"] = "This is ViewData";
ViewBag.Message = "This is ViewBag";
return View();
}
On view defined both as following.
<b>@ViewBag.Message</b>
@if(ViewData["Message"]!=null)
{
ViewData["Message"].ToString();
}
The output will show only one message and that will be the last one [in this case, message will be “This is ViewBag”].
TempData
TempData is also a dictionary object as ViewData and stores value in key/value pair. It is derived from TempDataDictionary. It is mainly used to transfer the data from one request to another request or we can say subsequent request. If the data for TempData has been read, then it will get cleaned. To persist the data, there are different ways. It all depends on how you read the data.
No Read Data
If you haven’t read the data in redirection process, then your data is available with the next subsequent request. You can see that in the following code, we have set up a TempData[“Emp” but neither read it in any action method nor in view.
So, once the “About” page renders and if we move to “Contact” page, the TempData[“Emp”] will be available.
Note
Do not read data on View.
public ActionResult Index()
{
Employee emp = new Employee() { Id = 1001, Name = "Peter", Address = "London", Age = 25 };
//Setting the TempData
TempData["Emp"] = emp;
return RedirectToAction("Index1");
}
public ActionResult Index1()
{
//Not reading TempData
return RedirectToAction("Index2");
}
public ActionResult Index2()
{
//Not reading TempData
return RedirectToAction("About");
}
public ActionResult About()
{
//Not reading TempData
return View();
}
public ActionResult Contact()
{
//Data will available here because we have not read data yet
var tempEmpData = TempData["Emp"];
return View();
}
Normal Data Read
If you read the data on “About” page when it will render and try to access the value on “Contact” page, it will not be available.
@{
ViewBag.Title = "About";
}
<h2>About Page</h2>
<br />
@{
var data = (MVCStateManagement.Models.Employee)TempData["Emp"];
}
TempData will not be available with Contact page because we have already read that data on “About” page. TempData is only available with subsequent request if you have not read yet.
public ActionResult Contact()
{
//Data will not available here because already read on About page
var tempEmpData = TempData["Emp"];
return View();
}
Keep TempData
If you still want to persist your data with the next request after reading it on “About” page that you can use “Keep()” method after reading data on “About” page. The Keep method will persist your data for next subsequent request.
@{
var data = (MVCStateManagement.Models.Employee)TempData["Emp"];
TempData.Keep();
}
public ActionResult Contact()
{
//TempData will available here because we have keep on about page
var tempEmpData = TempData["Emp"];
return View();
}
Peek TempData
Using Peek() method, we can directly access the TempData value and keep it for next subsequent request.
@{
var data = (MVCStateManagement.Models.Employee)TempData.Peek("Emp");
}
When we move to “Contact” page, the TempData will be available.
public ActionResult Contact()
{
//TempData will available because we have already keep data using Peek() method.
var tempEmpData = TempData["Emp"];
return View();
}
I hope this post helps you. Please share your feedback which will help me improve the next posts. If you have any doubts, please ask in the comments section.