In this article, we will look at how to manually customize an error page in ASP.NET MVC 5.

MVC Introduction
The MVC architectural pattern separates the user interface (UI) of an application into three main parts.
Model
A set of classes that describes the data you are working with as well as the business logic.
View
Defines how the application’s UI will be displayed. It is pure HTML, which decides how the UI is going to look.
Controller
A set of classes that handles communication from the user, overall application flow, and application-specific logic
When an HTTP request arrives for an MVC application, that request gets routed to a controller, and then it is up to the controller to talk to either the database, the file system, or the model.
Why do we need a Custom Error Page?
We would just configure our custom error pages in one place and it would just work, no matter how/where the error was raised. In order to handle exceptions thrown by your action methods, you need to mark your method with the HandleError attribute. The HandleError attribute also allows you to use a custom page for this error.
Steps to be Followed
Step 1
Create a MVC application named “Http500Test”.
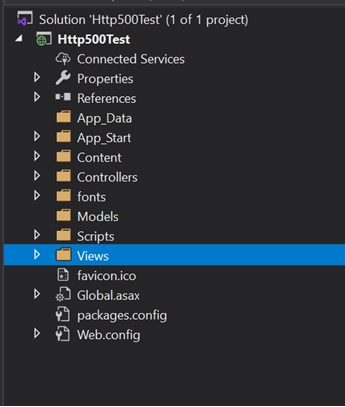
The solution looks like this
Step 2
Create a Controller class file named “CustomerErrorUserController.cs”
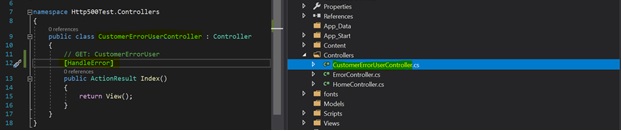
[HandleError] attribute provided built-in exception filters. This attribute can be applied over the action method as well as the controller or at the global level.
At CustomerErrorUser/Index, this application will show error.cshtml as the view not found in Index but in the web.config file. The error statusCode="404" means that the file is not found and it means the controller name or controller action method name is the issue.
[HandleError] //If I put in this attribute and run, it will go to the Customized by a Default error page.
Step 3
Create a controller class named “ErrorController.cs”
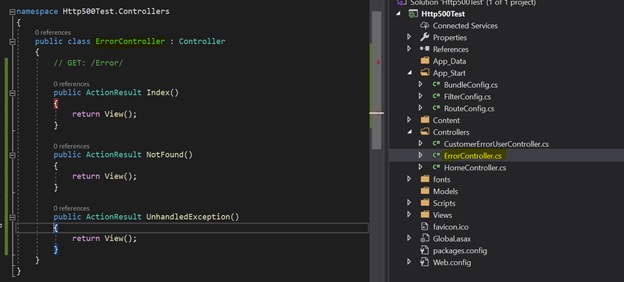
I have added two action methods – NotFound() and UnhandledException().
Step 4
Go to View/Shared Folder; create two views named “NotFound.cshtml” and “UnhandledException.cshtml”
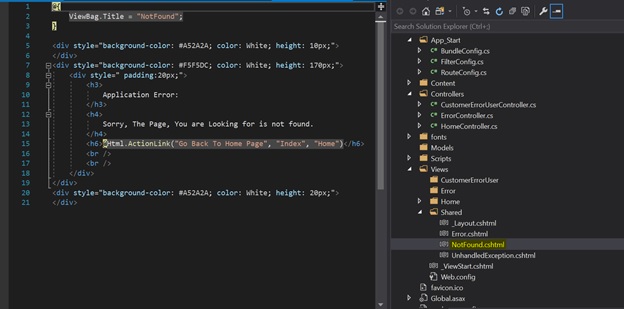
Put your own code in the NotFound.cshtml file by removing the existing code.
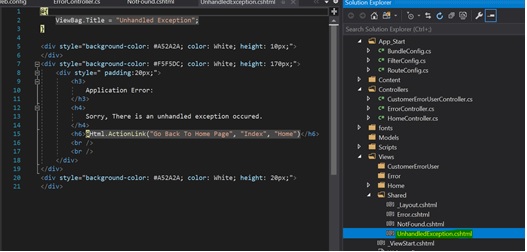
Put your own code in the UnhandledException.cshtml file by removing the existing code.
Step 5
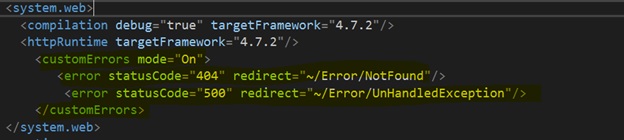
Go to Web.config and. Add some code for “File Not Found” and “UnhandledException”
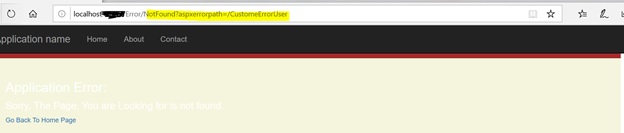
Output
http://localhost:63217/CustomeErrorUser
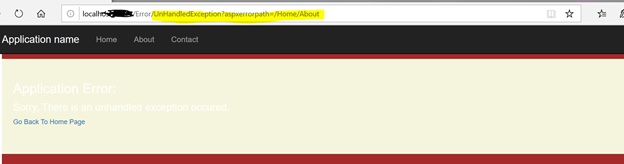
How to display UnhandledException?
I have added two lines of code in the About() action method in HomeController.cs
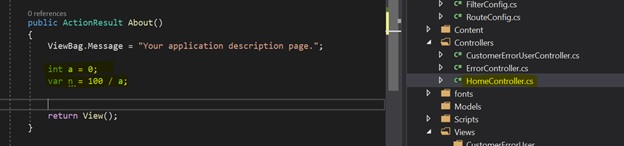
Now run this MVC app and click on “About”
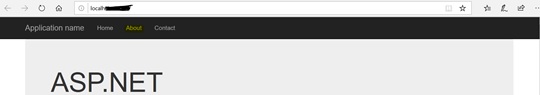
Output
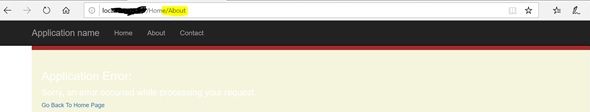
Instead of redirecting to “UnhandledException.cshtml”, the app is showing error.cshtml file
How to show UnhandledException.cshtml?
Visual Studio, by default, is creating two cshtml files, i.e. _Layout.cshtml and Error.cshtml inside the Shared folder.
Since we are using [HanldeError] attribute, all the unhandled exceptions will be redirected to by default error page (Error.cshtml).
There was some boilerplate code left in the FilterConfig.cs when creating the project.
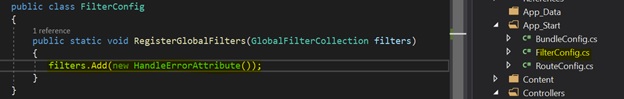
This creates a new instance of HandleErrorAttribute, which is applied globally to all of my views. With no customization, if a view throws an error while utilizing this attribute, MVC will display the default Error.cshtml file in the Shared folder.
Commenting this line out solved the problem and allowed me to use custom error pages for 500 errors.
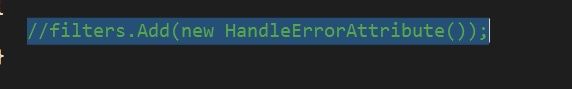
Again run the application and click on “About”
Thank you so much for watching the article. I hope this will be helpful. Please provide your comments in the box below.