What exactly is DataTables?
DataTables is a jQuery Javascript library plug-in. It is a highly flexible tool that adds advanced interaction controls to any HTML table. It is founded on the principles of progressive enhancement.

Let's begin with the database section.
Database Part
I've created a database called "Northwind" that contains a "Customers" entity.
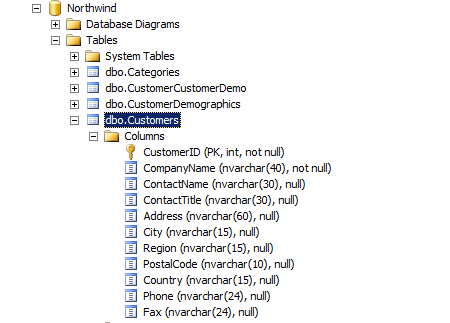
Next, we are going to create an ASP.NET MVC5 Web application.
Creating ASP.NET MVC5 Web Application
Open New Visual Studio 2015 IDE.
After opening IDE just, next we are going to create MVC project for doing that just click File - inside that New - Project.
After choosing a project, a new dialog will pop up with the name “New Project”. In that, we are going to choose Visual C# Project Templates - Web - ASP.NET Web Application. Then, we are going to name the project as “DemoDatatables”.
After naming the project we are going click on OK button to create a project.
A new dialog will pop up for choosing templates for Creating “ASP.NET Web Application;” in that template, we are going to Create MVC application. That's why we are going to choose “MVC template” and next click on OK button to create a project.
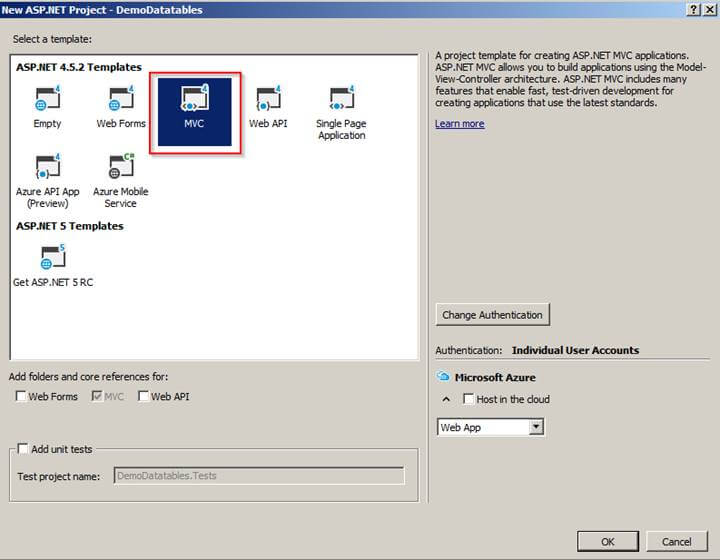
After clicking on OK button it will start to create a project.
Project Structure
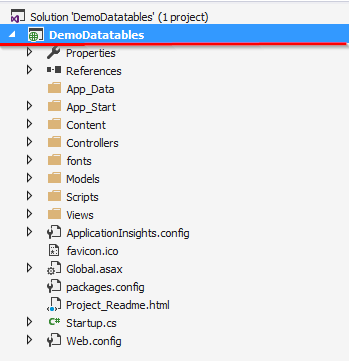
After creating project next, we are going to create Model.
Creating Customer Model
We are going to add Customer Model to the Models folder.
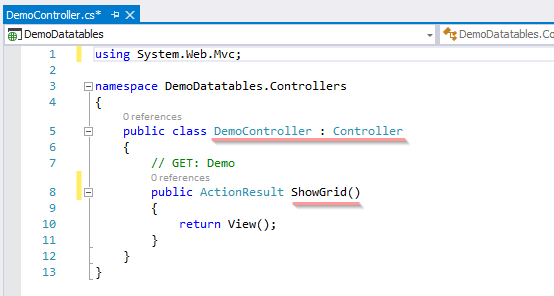
After adding Action Method now let add View with name “ShowGrid”.
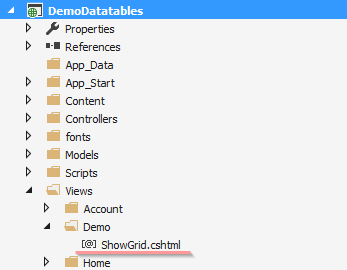
Adding DataTables Grid Scripts and Css on ShowGrid View
In first step we are going to add Script and Css reference.
<script src="//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.11.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<link href="~/Content/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.10.15/css/dataTables.bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.datatables.net/responsive/2.1.1/css/responsive.bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<script src="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.10.15/js/jquery.dataTables.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.10.15/js/dataTables.bootstrap4.min.js "></script>
After adding Script and CSS reference next we are going to add DataTables Markup.
Adding DataTables Markup
It is simple Html Table in that we are going to add columns headers (“<th>”) with all the columns names which we want to display on the grid.
After adding Markup next, we are going to add DataTables function to Create DataTables.
<div class="container">
<br />
<div style="width:90%; margin:0 auto;">
<table id="demoGrid" class="table table-striped table-bordered dt-responsive nowrap" width="100%" cellspacing="0">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>CustomerID</th>
<th>CompanyName</th>
<th>ContactName</th>
<th>ContactTitle</th>
<th>City</th>
<th>PostalCode</th>
<th>Country</th>
<th>Phone</th>
<th>Edit</th>
<th>Delete</th>
</tr>
</thead>
</table>
</div>
</div>
Adding DataTables Function to create DataTables
Code Snippet
<script>
$('#demoGrid').dataTable({
});
</script>
DataTables Options
- Processing - Enable or disable the display of a 'processing' indicator when the table is being processed (e.g. a sort).
- server Side - Server-side processing - where filtering, paging, and sorting calculations are all performed by a server.
- Filter - this option is used for enabling and disabling of search box
- orderMulti - When ordering is enabled (ordering), by default DataTables allows users to sort multiple columns by shift-clicking upon the header cell for each column. Although this can be quite useful for users, it can also increase the complexity of the order, potentiality increasing the processing time of ordering the data. Therefore, this option is provided to allow this shift-click multiple column abilities
- Ajax - Ajax request is made to get data to DataTables.
- columnDefs - Set column definition initialisation properties.
- Columns - Set column specific initialisation properties.
After completing with an understanding of options or properties next we are going to set it.
We are going to set “processing” option to true to display processing bar, after that, we are going to set the “serverSide” option to true because we are going to do paging and filtering at serverSide.
Next options after “serverSide” option are “filter.” We are going to use the search box; that's why we have set this property to true, “orderMulti” is also set to false because we do not want to sort multiple columns at once.
DataTables Options snapshot

Ajax Option
And the main option is Ajax which we are going to use for calling an Action Method for getting data to bind DataTables Grid the data is in Json format. For that we are going to pass URL: -"/Demo/LoadData”, this request is Post request. And data type we are going to set as Json.
We are going to call LoadData Action Method which is under Demo Controller which I will explain in upcoming steps.

columnDefs Option
After setting Ajax we have a “columnDefs” option which I have used for hiding Primary key of the table (“CustomerID”) and which should also be not searchable.

columns Option
Finally, the second to last option is columns which are used for initialization of DataTables grid. Add that property which you need to render on the grid, which must be defined in this columns option.
Finally, on click of the delete button, we can call a custom function to delete data as I have created “DeleteData” function.
Complete code Snippet of ShowGrid View
@{
Layout = null;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>ShowGrid</title>
<script src="//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.11.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<link href="~/Content/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.10.15/css/dataTables.bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.datatables.net/responsive/2.1.1/css/responsive.bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<script src="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.10.15/js/jquery.dataTables.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.10.15/js/dataTables.bootstrap4.min.js "></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function () {
$("#demoGrid").DataTable({
"processing": true, // for show progress bar
"serverSide": true, // for process server side
"filter": true, // this is for disable filter (search box)
"orderMulti": false, // for disable multiple column at once
"pageLength": 5,
"ajax": {
"url": "/Demo/LoadData",
"type": "POST",
"datatype": "json"
},
"columnDefs":
[{
"targets": [0],
"visible": false,
"searchable": false
},
{
"targets": [7],
"searchable": false,
"orderable": false
},
{
"targets": [8],
"searchable": false,
"orderable": false
},
{
"targets": [9],
"searchable": false,
"orderable": false
}],
"columns": [
{ "data": "CustomerID", "name": "CustomerID", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "CompanyName", "name": "CompanyName", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "ContactName", "title": "ContactName", "name": "ContactName", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "ContactTitle", "name": "ContactTitle", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "City", "name": "City", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "PostalCode", "name": "PostalCode", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "Country", "name": "Country", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "Phone", "name": "Phone", "title": "Status", "autoWidth": true },
{
"render": function (data, type, full, meta)
{ return '<a class="btn btn-info" href="/Demo/Edit/' + full.CustomerID + '">Edit</a>'; }
},
{
data: null, render: function (data, type, row) {
return "<a href='#' class='btn btn-danger' onclick=DeleteData('" + row.CustomerID + "'); >Delete</a>";
}
},
]
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<br />
<div style="width:90%; margin:0 auto;">
<table id="demoGrid" class="table table-striped table-bordered dt-responsive nowrap" width="100%" cellspacing="0">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>CustomerID</th>
<th>CompanyName</th>
<th>ContactName</th>
<th>ContactTitle</th>
<th>City</th>
<th>PostalCode</th>
<th>Country</th>
<th>Phone</th>
<th>Edit</th>
<th>Delete</th>
</tr>
</thead>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
After completing with initialization of DataTables grid next we are going to create LoadData Action Method.
Adding LoadData Action Method to Demo Controller
Here we are going to Add Action Method with name LoadData. In this action method, we are going to get all Customer records from the database to display and on the basis of the parameter we are going sort data, and do paging with data.
We are doing paging and filtering of data on the server side; that why we are using IQueryable which will execute queries with filters on the server side.
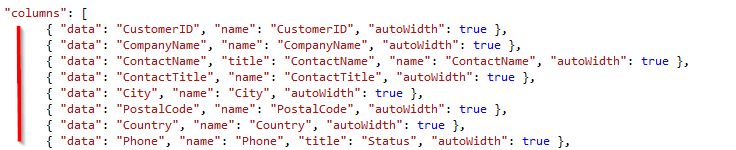
Render buttons in Columns
At last, we need to render button in the grid for editing data and deleting data.
@{
Layout = null;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>ShowGrid</title>
<script src="//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.11.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<link href="~/Content/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.10.15/css/dataTables.bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.datatables.net/responsive/2.1.1/css/responsive.bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<script src="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.10.15/js/jquery.dataTables.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.10.15/js/dataTables.bootstrap4.min.js "></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function () {
$("#demoGrid").DataTable({
"processing": true, // for show progress bar
"serverSide": true, // for process server side
"filter": true, // this is for disable filter (search box)
"orderMulti": false, // for disable multiple column at once
"pageLength": 5,
"ajax": {
"url": "/Demo/LoadData",
"type": "POST",
"datatype": "json"
},
"columnDefs":
[{
"targets": [0],
"visible": false,
"searchable": false
},
{
"targets": [7],
"searchable": false,
"orderable": false
},
{
"targets": [8],
"searchable": false,
"orderable": false
},
{
"targets": [9],
"searchable": false,
"orderable": false
}],
"columns": [
{ "data": "CustomerID", "name": "CustomerID", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "CompanyName", "name": "CompanyName", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "ContactName", "title": "ContactName", "name": "ContactName", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "ContactTitle", "name": "ContactTitle", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "City", "name": "City", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "PostalCode", "name": "PostalCode", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "Country", "name": "Country", "autoWidth": true },
{ "data": "Phone", "name": "Phone", "title": "Status", "autoWidth": true },
{
"render": function (data, type, full, meta)
{ return '<a class="btn btn-info" href="/Demo/Edit/' + full.CustomerID + '">Edit</a>'; }
},
{
data: null, render: function (data, type, row) {
return "<a href='#' class='btn btn-danger' onclick=DeleteData('" + row.CustomerID + "'); >Delete</a>";
}
},
]
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<br />
<div style="width:90%; margin:0 auto;">
<table id="demoGrid" class="table table-striped table-bordered dt-responsive nowrap" width="100%" cellspacing="0">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>CustomerID</th>
<th>CompanyName</th>
<th>ContactName</th>
<th>ContactTitle</th>
<th>City</th>
<th>PostalCode</th>
<th>Country</th>
<th>Phone</th>
<th>Edit</th>
<th>Delete</th>
</tr>
</thead>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
After completing with initialization of DataTables grid next we are going to create LoadData Action Method.
Adding LoadData Action Method to Demo Controller
Here we are going to Add Action Method with name LoadData. In this action method, we are going to get all Customer records from the database to display and on the basis of the parameter we are going sort data, and do paging with data.
We are doing paging and filtering of data on the server side; that why we are using IQueryable which will execute queries with filters on the server side.
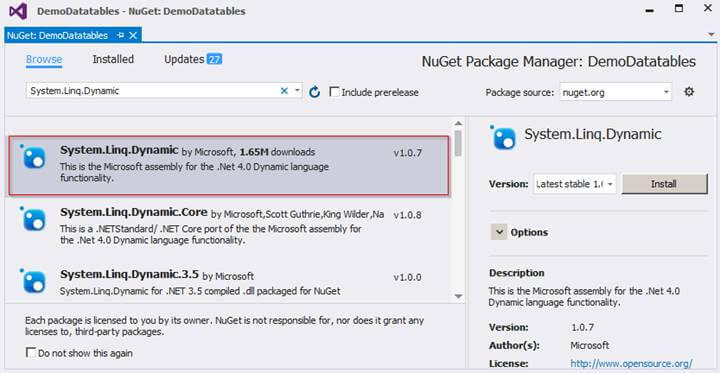
For using OrderBy in the query we need to install System.Linq.Dynamic package from NuGet packages.
Snapshot while adding System.Linq.Dynamic package from NuGet packages
After adding the package, next, we see the complete code snippet and how to get data and do paging and filtering with it.
Complete code Snippet of LoadData Action Method
All processes are step by step with comments; so it's easy to understand.
All Request.Form.GetValues parameters value will get populated when AJAX post method gets called on a load of if you do paging or sorting and search.
Code Snippet
public ActionResult LoadData()
{
try
{
var draw = Request.Form.GetValues("draw").FirstOrDefault();
var start = Request.Form.GetValues("start").FirstOrDefault();
var length = Request.Form.GetValues("length").FirstOrDefault();
var sortColumn = Request.Form.GetValues("columns[" + Request.Form.GetValues("order[0][column]").FirstOrDefault() + "][name]").FirstOrDefault();
var sortColumnDir = Request.Form.GetValues("order[0][dir]").FirstOrDefault();
var searchValue = Request.Form.GetValues("search[value]").FirstOrDefault();
//Paging Size (10,20,50,100)
int pageSize = length != null ? Convert.ToInt32(length) : 0;
int skip = start != null ? Convert.ToInt32(start) : 0;
int recordsTotal = 0;
// Getting all Customer data
var customerData = (from tempcustomer in _context.Customers
select tempcustomer);
//Sorting
if (!(string.IsNullOrEmpty(sortColumn) && string.IsNullOrEmpty(sortColumnDir)))
{
customerData = customerData.OrderBy(sortColumn + " " + sortColumnDir);
}
//Search
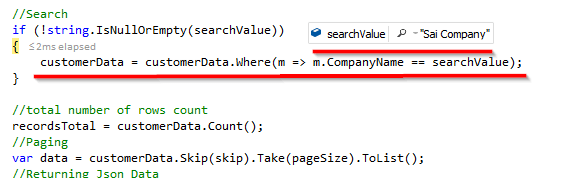
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(searchValue))
{
customerData = customerData.Where(m => m.CompanyName == searchValue);
}
//total number of rows count
recordsTotal = customerData.Count();
//Paging
var data = customerData.Skip(skip).Take(pageSize).ToList();
//Returning Json Data
return Json(new { draw = draw, recordsFiltered = recordsTotal, recordsTotal = recordsTotal, data = data });
}
catch (Exception)
{
throw;
}
}
Complete code Snippet of DemoController
using DemoDatatables.Models;
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.Linq.Dynamic;
using System.Data.Entity;
namespace DemoDatatables.Controllers
{
public class DemoController : Controller
{
// GET: Demo
public ActionResult ShowGrid()
{
return View();
}
public ActionResult LoadData()
{
try
{
//Creating instance of DatabaseContext class
using (DatabaseContext _context = new DatabaseContext())
{
var draw = Request.Form.GetValues("draw").FirstOrDefault();
var start = Request.Form.GetValues("start").FirstOrDefault();
var length = Request.Form.GetValues("length").FirstOrDefault();
var sortColumn = Request.Form.GetValues("columns[" + Request.Form.GetValues("order[0][column]").FirstOrDefault() + "][name]").FirstOrDefault();
var sortColumnDir = Request.Form.GetValues("order[0][dir]").FirstOrDefault();
var searchValue = Request.Form.GetValues("search[value]").FirstOrDefault();
//Paging Size (10,20,50,100)
int pageSize = length != null ? Convert.ToInt32(length) : 0;
int skip = start != null ? Convert.ToInt32(start) : 0;
int recordsTotal = 0;
// Getting all Customer data
var customerData = (from tempcustomer in _context.Customers
select tempcustomer);
//Sorting
if (!(string.IsNullOrEmpty(sortColumn) && string.IsNullOrEmpty(sortColumnDir)))
{
customerData = customerData.OrderBy(sortColumn + " " + sortColumnDir);
}
//Search
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(searchValue))
{
customerData = customerData.Where(m => m.CompanyName == searchValue);
}
//total number of rows count
recordsTotal = customerData.Count();
//Paging
var data = customerData.Skip(skip).Take(pageSize).ToList();
//Returning Json Data
return Json(new { draw = draw, recordsFiltered = recordsTotal, recordsTotal = recordsTotal, data = data });
}
}
catch (Exception)
{
throw;
}
}
}
}
Save the entire Source code and run the application.
Run Application
To access the application, enter URL - http://localhost:#####/demo/showgrid .
“#####” is localhost port number.
Real-time Debugging Snapshot
In this section, you can see what values are populated when post method gets called.

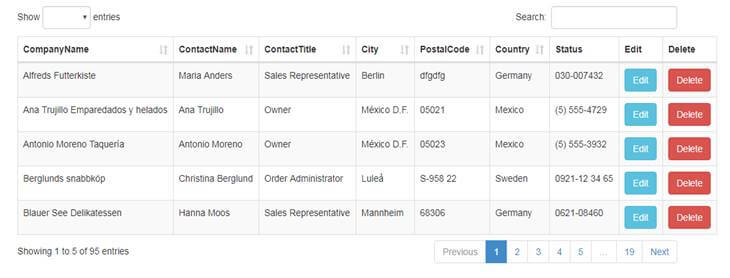
Search with DataTables grid
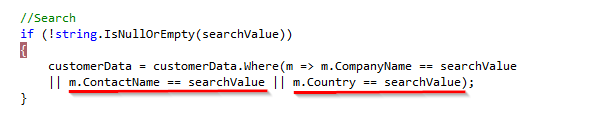
In this section we have implemented a search for only Companyname column, if you want to add another column just use or condition (“||”) with it.

Adding more columns to search
Debugging View of Search
After completing with search Implementation next we are going to work on Edit Button of DataTables Grid.
Edit Event in DataTables grid
In this section first we are going add Edit Action Method in Demo Controller which will handle edit request and it will take Customer ID as input from which we are going to get details of that customer.
Code Snippet of Edit Action Method
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult Edit(int? ID)
{
try
{
using (DatabaseContext _context = new DatabaseContext())
{
var Customer = (from customer in _context.Customers
where customer.CustomerID == ID
select customer).FirstOrDefault();
return View(Customer);
}
}
catch (Exception)
{
throw;
}
}
After having a look on Edit action method next let’s see how to render Edit link (button).
Below is syntax for rendering Edit button
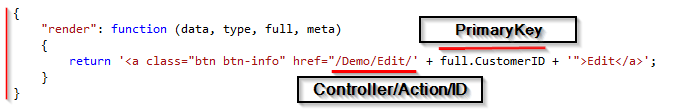
Finally, you can see Edit View.
After completing with Edit part next we are going to have a look at delete part.
Delete Event in DataTables grid
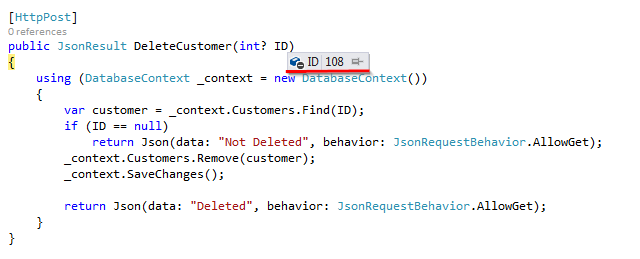
In this section first we are going add DeleteCustomer Action Method in DemoController which will handle delete request and it will take Customer ID (“ID”) as input from which we are going to delete customer data.
Code Snippet of DeleteCustomer
[HttpPost]
public JsonResult DeleteCustomer(int? ID)
{
using (DatabaseContext _context = new DatabaseContext())
{
var customer = _context.Customers.Find(ID);
if (ID == null)
return Json(data: "Not Deleted", behavior: JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
_context.Customers.Remove(customer);
_context.SaveChanges();
return Json(data: "Deleted", behavior: JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
}
After having a look on DeleteCustomer action method next let’s see how to render delete link (button).
Below is syntax for rendering Delete button
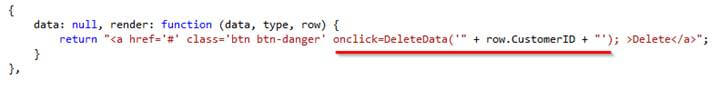
Now you can see that we are generating simple href button and on that button, we have added an onclick event to call DeleteData function which we have not created yet, so let’s create DeleteData function.
Code Snippet
In this part when user clicks on Delete button DeleteData function will get called and first thing it will show is confirmation alert ("Are you sure you want to delete ...?") if you click on ok (confirm) button then it will call Delete function. This function takes CustomerID as input, next we are generating URL of DeleteCustomer Action Method and passing it as ajax post request and along with it we are passing Customer ID as parameter.
If data is deleted, then we are going to get “Deleted” as a response from Deletecustomer Action Method, finally, we show alert to the user and reload grid.
<script>
function DeleteData(CustomerID) {
if (confirm("Are you sure you want to delete ...?")) {
Delete(CustomerID);
}
else {
return false;
}
}
function Delete(CustomerID) {
var url = '@Url.Content("~/")' + "Demo/DeleteCustomer";
$.post(url, { ID: CustomerID }, function (data) {
if (data == "Deleted") {
alert("Delete Customer !");
oTable = $('#demoGrid').DataTable();
oTable.draw();
}
else {
alert("Something Went Wrong!");
}
});
}
</script>
Debugging View while deleting customer
Finally, we have learned how to use jQuery DataTables Grid with ASP.NET CORE MVC. I hope you enjoyed the article.