1. Create your database
Using the following script, create the UserProfile table

CREATE TABLE UserProfile
(
UserId INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1, 1),
UserName VARCHAR(50),
Password VARCHAR(50),
IsActive BIT
);
Insert user records using the following script:
INSERT INTO UserProfile (UserName, Password, IsActive)
VALUES ('Peter', 'Peter1234', 1),
('Scott', 'Scott1234', 1),
('Alex', 'Alex1234', 1);
2. Create Project
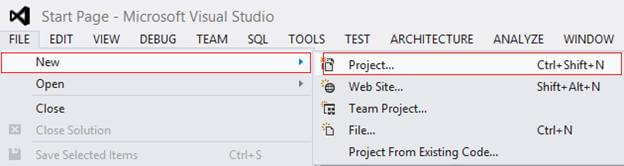
Go to File, New, then click on Project.
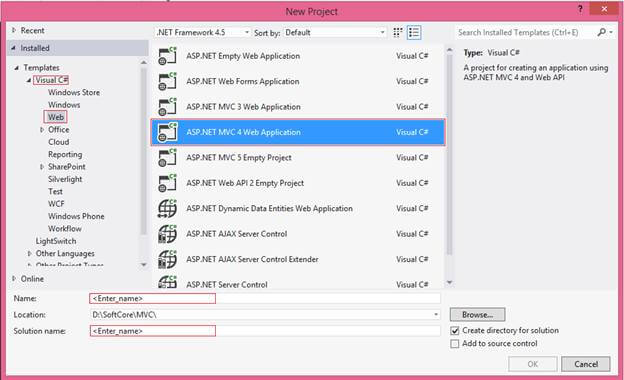
Select Visual C#, Web under Installed templates. After that, select ASP.NET MVC 4 Web Application, then mention the Application Name (MvcLoginAppDemo) and Solution Name as you wish, then click OK.
Under Project template, select a template as Basic, then view the engine as Razor. Click OK.
3. Include an Entity Data Model
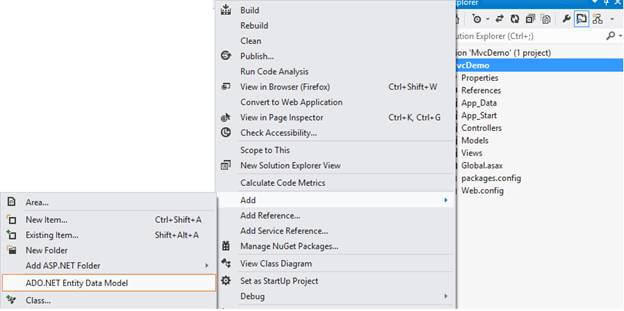
Navigate to Solution Explorer, select Project, Add, and then ADO.NET Entity Data Model.
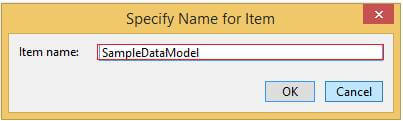
Give it a meaningful model name, and then click on Add.
Select Generate from the database and then click on Next.
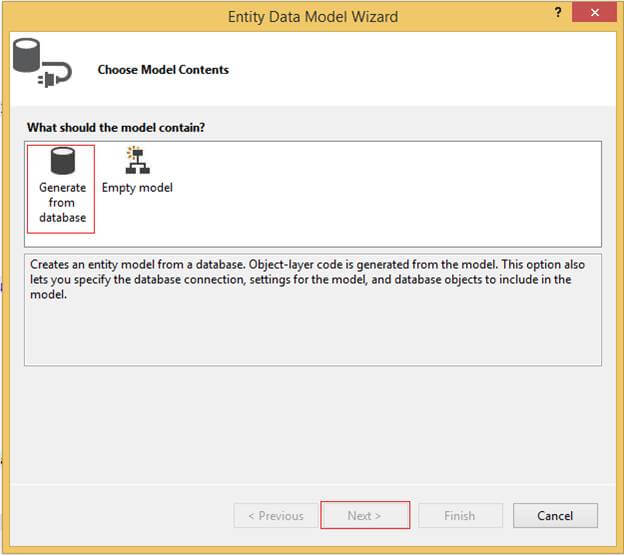
Click on New Connection.
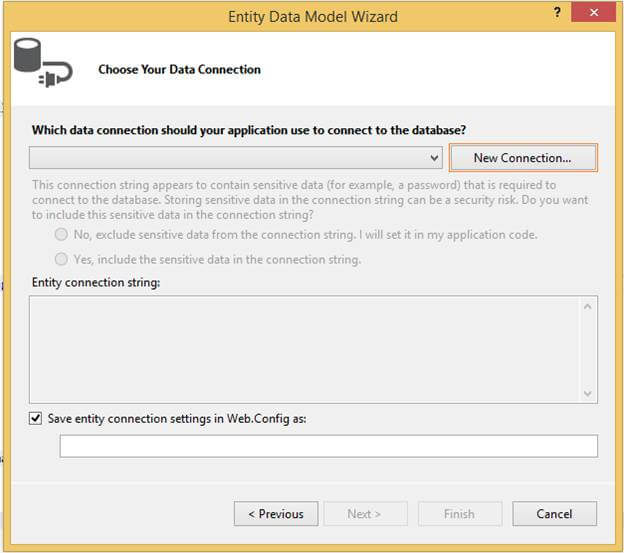
After clicking on New Connection, we have to provide the following Connection Properties in the following wizard.
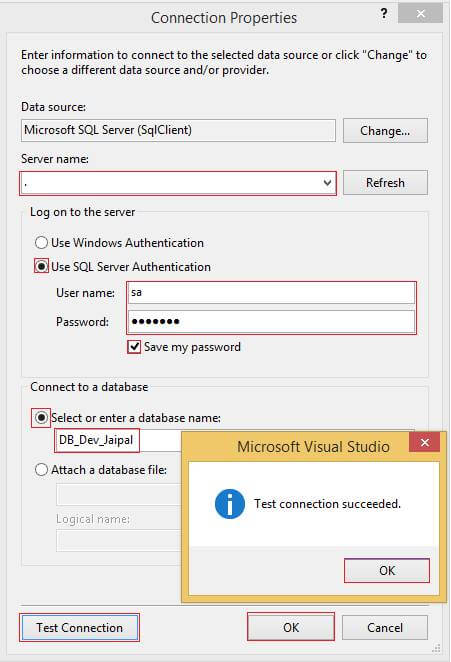
Provide the Server name.
- Select the "Use SQL Server Authentication" radio button.
- Enter the Username and Password in the password text box.
- Check the "Save my password" checkbox.
- Select the "Select or enter a database name:" radio button.
- Select the database to which you want to set the connection.
- Click on the "Test Connection" button to ensure the connection can be established.
- Then click OK.
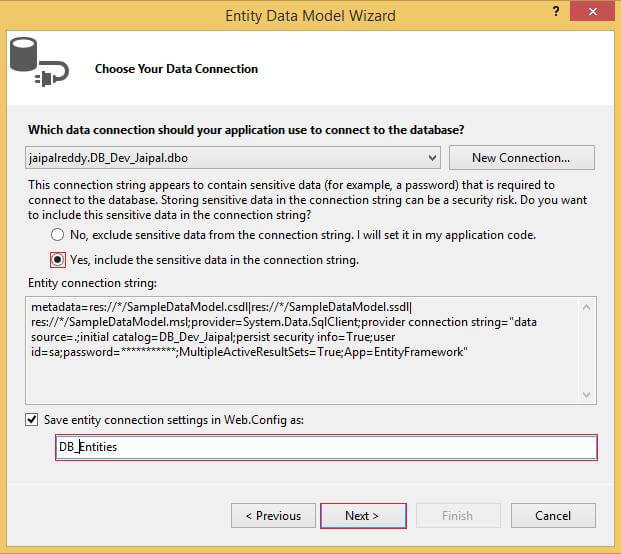
Select the radio button, and yes, include the sensitive data in the connection string.
Choose your database objects, as in the following image.
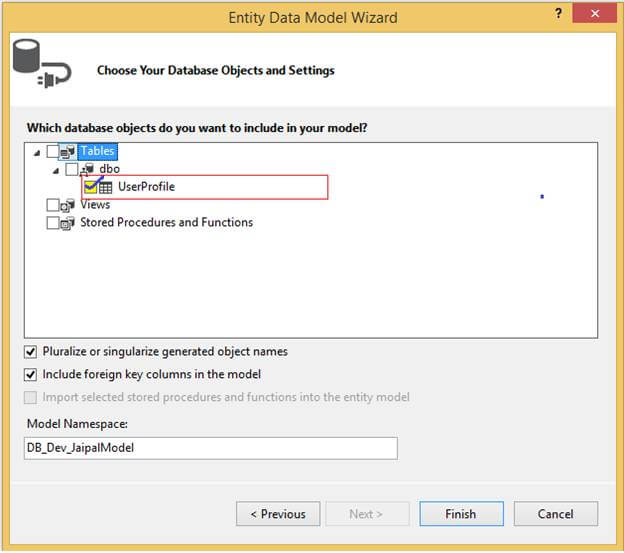
Click on Finish. At this point UserProfie entity will be created.
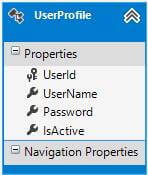
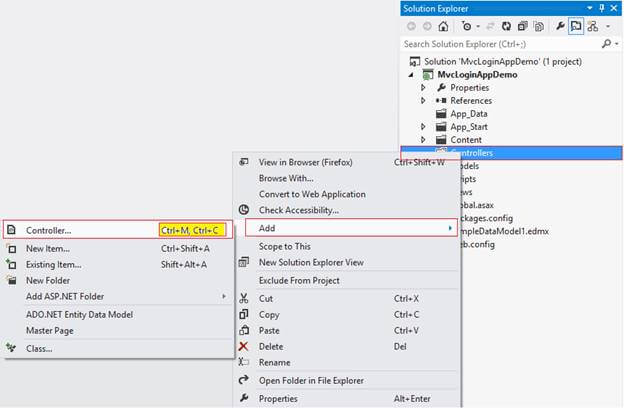
4. Add a Controller
Go to Solution Explorer, right-click on the Controller folder, Add, and then click on Controller.
( Or ) Simply use shortcut key Ctrl + M, Ctrl + C,
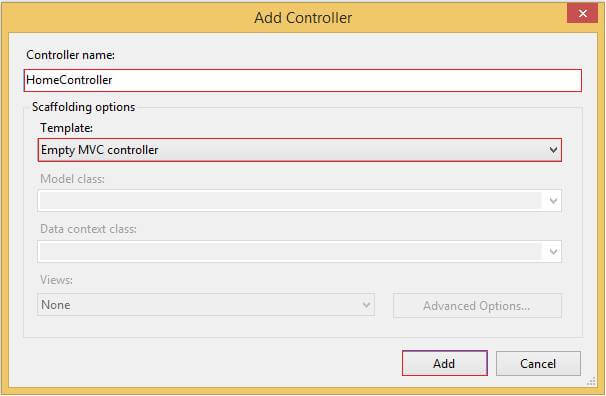
Provide the Controller Name and Scaffolding template as Empty MVC Controller. Then click on Add.
Write the following code in HomeController.
using System.Linq;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace MvcLoginAppDemo.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
public ActionResult Login()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Login(UserProfile objUser)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
using (DB_Entities db = new DB_Entities())
{
var obj = db.UserProfiles.Where(a => a.UserName.Equals(objUser.UserName) && a.Password.Equals(objUser.Password)).FirstOrDefault();
if (obj != null)
{
Session["UserID"] = obj.UserId.ToString();
Session["UserName"] = obj.UserName.ToString();
return RedirectToAction("UserDashBoard");
}
}
}
return View(objUser);
}
public ActionResult UserDashBoard()
{
if (Session["UserID"] != null)
{
return View();
}
else
{
return RedirectToAction("Login");
}
}
}
}
5. Create Views
Create View for Login Action Method
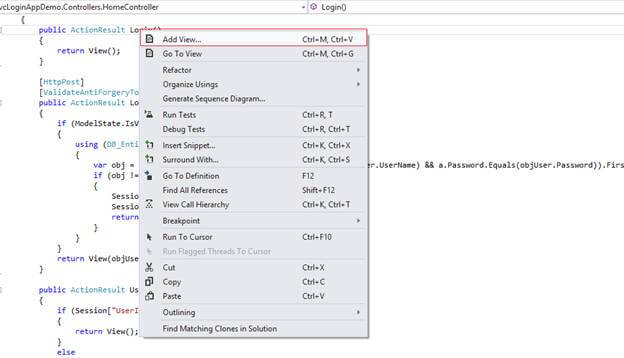
Right-click on the Login Action method, then click on Add View, as in the following picture.
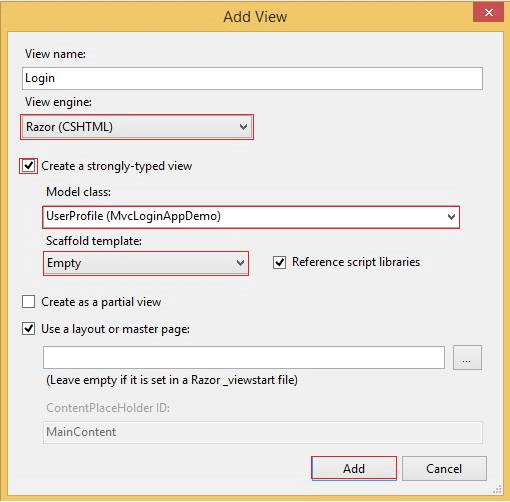
Create a Strongly Typed View
View Name must be an action method name.
Select the view engine as Razor.
Select Create a strongly typed view CheckBox.
Select Model class as UserProfile (MvcLoginAppDemo)
Select the Scaffold template as Empty
Click on Add
Write the following code in Login.cshtml (view).
@model MvcLoginAppDemo.UserProfile
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Login";
}
@using (Html.BeginForm("Login", "Home", FormMethod.Post))
{
<fieldset>
<legend>Mvc Simple Login Application Demo</legend>
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
@Html.ValidationSummary(true)
@if (ViewBag.Message != null)
{
<p style="border: 1px solid red">
@ViewBag.Message
</p>
}
<table>
<tr>
<td>@Html.LabelFor(a => a.UserName)</td>
<td>@Html.TextBoxFor(a => a.UserName)</td>
<td>@Html.ValidationMessageFor(a => a.UserName)</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>@Html.LabelFor(a => a.Password)</td>
<td>@Html.PasswordFor(a => a.Password)</td>
<td>@Html.ValidationMessageFor(a => a.Password)</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td><input type="submit" value="Login" /></td>
<td></td>
</tr>
</table>
</fieldset>
}
Create View for UserDashBoard Action method same as login view. And write the following code in UserDashBoard.cshtml (View).
@{
ViewBag.Title = "UserDashboard";
}
<fieldset>
<legend>User Dashboard</legend>
@if (Session["UserName"] != null)
{
<text>Welcome @Session["UserName"].ToString()</text>
}
</fieldset>
6. Set as StartUp Page
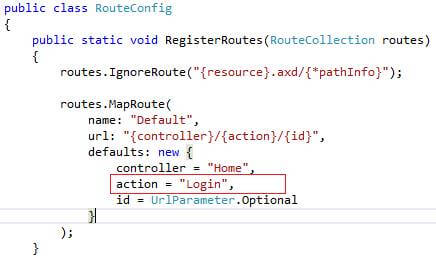
Go to Solution Explorer, Project, App_Start, then RouteConfig.cs, and change the action name from Index to Login (Login. cshtml as start-up page).
7. Run the Application
Provide the user credentials and click on OK. If you provide valid user credentials, then the user name will be displayed on your dashboard.